Introduction
Contiguous memory allocation is a fundamental concept in memory management. Its simplicity makes it suitable for certain types of systems, especially where performance is less critical. However, its tendency to cause fragmentation and inefficient use of memory makes it less suitable for modern, complex systems.
Contiguous memory allocation is a memory management technique where each process is allocated a single contiguous block of memory. This method ensures that a process's memory is allocated in one continuous segment.
Principles of Contiguous Memory Allocation:
Fixed Partitioning: Memory is divided into fixed-size partitions at system initialization. Each partition can hold exactly one process.
Variable Partitioning: Memory is divided into variable-sized partitions. Each process gets exactly as much memory as it needs.
Fragmentation:
Internal Fragmentation: Occurs when allocated memory may have some unused space (e.g., if a fixed-size partition is larger than the process size). More prevalent in fixed partitioning schemes.
External Fragmentation: Occurs when free memory is divided into small blocks scattered throughout the memory. More prevalent in dynamic partitioning schemes.
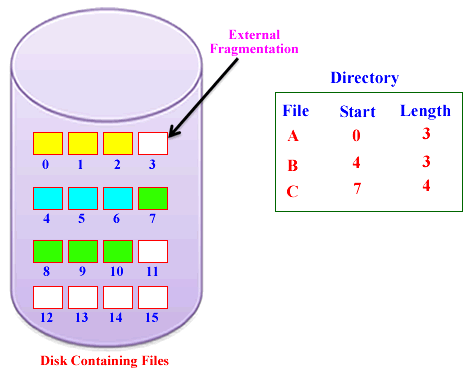
For both fixed and dynamic memory allocation schemes, the operating system must keep a list of each memory location,
noting which are free and which are occupied. As new jobs come into the system, the free partitions must be allocated.
These partitions can be allocated in four ways:
First Fit: The first fit algorithm scans memory from the beginning and allocates the first block that is large enough to fulfill the process's needs.
- It is generally fast because it stops searching as soon as it finds a suitable block.
- It can lead to fragmentation, as it leaves small unusable holes throughout the memory.
Best Fit: The best fit algorithm searches the entire list of available memory blocks and allocates the smallest block that is large enough to fulfill the process's needs.
- It reduces wasted space by allocating the smallest adequate block, potentially minimizing fragmentation.
- It increases fragmentation and allocation time, adds complexity, and can lead to poor memory utilization.
Worst Fit: The worst fit algorithm searches the entire list of available memory blocks and allocates the largest block. The idea is that the remaining space will be large enough to be useful for other processes.
- It can reduce the likelihood of creating small, unusable holes in memory.
- It is also slower than the first fit because it must search the entire list of memory blocks. Over time, it may lead to inefficient use of memory as large blocks get divided.
Next Fit: Next fit memory allocation is a variant of the first fit memory allocation algorithm used in dynamic memory management. Both of these algorithms are strategies for allocating memory blocks to processes in a way that attempts to minimize fragmentation and optimize performance.
- By continuing the search from the last allocation point, next fit can help reduce fragmentation compared to first fit. It avoids repeatedly filling up the beginning of the memory space while leaving the end underutilized.
- It might not always allocate the most optimal block because it stops at the first fit it finds, which could lead to inefficient use of memory.
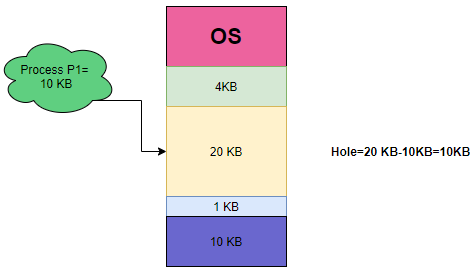
Example: Suppose we have the following memory partitions:
| 4 KB | 20 KB | 1 KB | 10 KB |
Process P1 of size 10KB has arrived and then the first hole that is enough to meet the requirements of size 20KB is chosen and allocated to the process.
Advantages :
Disadvantages :
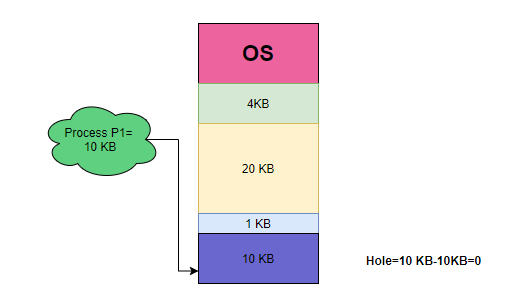
Example: Suppose we have the following memory partitions:
| 4 KB | 20 KB | 1 KB | 10 KB |
Process P1 of size 10KB is arrived and then the smallest hole to meet the requirements of size 10 KB is chosen and allocated to the process.
Advantages :
Disadvantages :
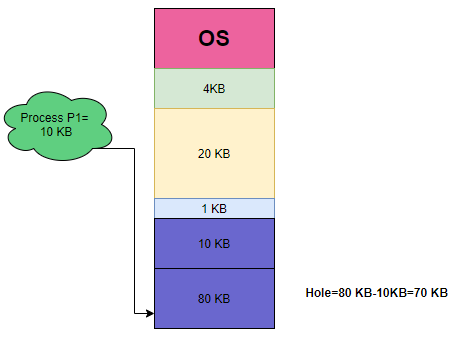
Example: Suppose we have the following memory partitions:
| 4 KB | 20 KB | 1 KB | 10 KB |
Process P1 of size 10KB has arrived and then the largest hole of size 80 KB is chosen and allocated to the process.
Advantages :
Disadvantages :
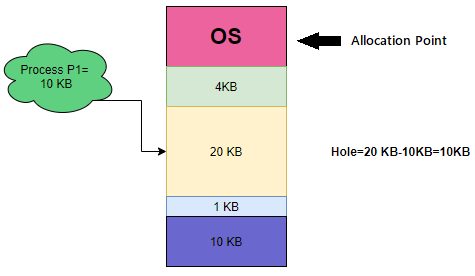
Example: Suppose we have the following memory partitions:
| 4 KB | 20 KB | 1 KB | 10 KB |
The Next Fit strategy will start searching from the first partition, Process P1 is allocated to the 20 KB partition, starting from the last allocation point.
Advantages :
Disadvantages :
Applications
- Process Management
- Memory Segmentation
- Disk Storage
- Networking
