Introduction to Star-Delta Starter for 3-Phase Induction Motor
A 3-phase induction motor is an essential component in many
industrial applications due to its high efficiency, robustness, and
simplicity. However, directly starting such motors can result in
high inrush currents, causing voltage drops and mechanical stress.
To mitigate these issues, an automatic star-delta starter is used.
This starter initially connects the motor windings in a star
configuration to reduce the starting current and torque, and then
switches to a delta configuration for normal operation.
The objective of this experiment is to design and implement a logic for starting a 3-phase induction motor using an automatic star-delta starter. The experiment involves the use of a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) to control the switching between star and delta configurations, as well as to handle start, stop, and trip conditions.
Star-Delta Starter
The star-delta starter is an electromechanical switch used to start
induction motors by reducing the initial starting current and
torque. The motor initially starts in a star configuration, where
the windings are connected in such a way that each winding receives
a reduced voltage. After a predetermined time, the windings are
reconfigured to a delta arrangement, where each winding receives the
full line voltage, allowing the motor to run at its rated speed and
torque.
Components:
1. Contactors (Y1, Y2, Y3):
● Main Contactor (K1): Connects the motor to the power supply.
● Star Contactor (K2): Connects motor windings in star configuration.
● Delta Contactor (K3): Connects motor windings in delta
configuration.
2. Timer: Controls the duration for which the motor remains in the star configuration before switching to delta.
3. Overload Relay: Protects the motor from overcurrent conditions.
4. Push Buttons:
● Start Button (PB1): Initiates the start sequence.
● Stop Button (PB2): Stops the motor.
5. Indicators: Visual indicators (LEDs) to show the status of the motor (starting, running, and fault conditions).
Circuit Description
The provided diagrams illustrate the control and power circuits for the star-delta starter controlled by a PLC.
Disadvantages of Unipolar PWM Single Phase Inverter
Control Circuit (Figure 1)
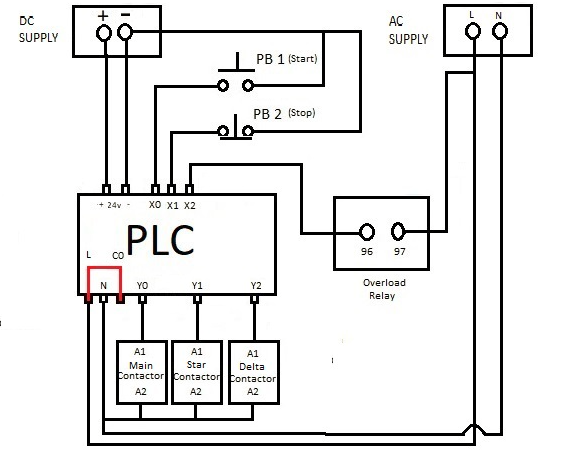
● The PLC inputs (X0, X1, X2) are connected to the start button
(PB1), stop button (PB2), and overload relay, respectively.
● The PLC outputs (Y0, Y1, Y2) control the main contactor, star
contactor, and delta contactor, respectively.
● The circuit is powered by a DC supply for the control logic and an
AC supply for the motor operation.
Disadvantages of Unipolar PWM Single Phase Inverter
Power Circuit (Figure 2)
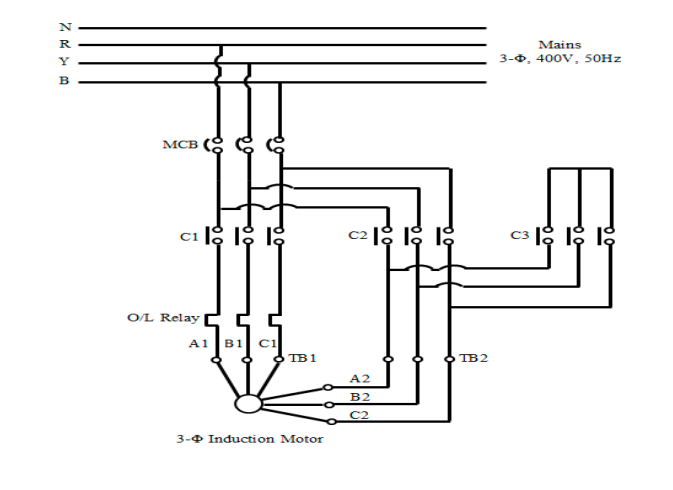
● The power circuit consists of the main contactor (C1), star
contactor (C2), and delta contactor (C3).
● The motor windings are initially connected in a star configuration
through the star contactor and then switched to a delta
configuration through the delta contactor.
PLC Logic (Figure 3)
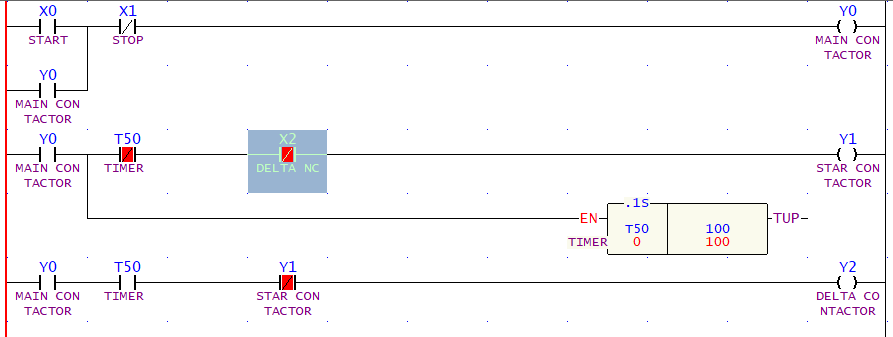
● The ladder diagram in Figure 3 represents the PLC logic for
controlling the star-delta starter.
● The start button (X0) initiates the sequence, while the stop
button (X1) halts the operation.
● The timer function is implemented in the PLC to manage the
transition from star to delta configuration.
Advantages
1. Reduced Starting Current: The star-delta starter significantly
reduces the starting current, minimizing voltage drops and
mechanical stress.
2. Cost-Effective: It is a cost-effective method compared to other
soft starting techniques.
3. Smooth Operation: Provides a smooth transition from start to full
speed operation, protecting the motor and the connected
equipment.
4. Ease of Implementation: The use of PLC for control logic allows
for easy implementation and customization.
Applications
1. Industrial Machinery: Widely used in starting large motors in
industries like manufacturing, textiles, and petrochemicals.
2. Pumps and Compressors: Commonly employed in starting large pumps
and compressors to avoid high inrush currents.
3. HVAC Systems: Used in large heating, ventilation, and air
conditioning systems.
4. Conveyor Systems: Applied in conveyor systems to ensure smooth
startup and operation.
Implementing an automatic star-delta starter using PLC provides an efficient and reliable method for starting 3-phase induction motors. By reducing the initial starting current and providing a smooth transition to full load operation, this method ensures the longevity and optimal performance of the motor and the connected system.
